
Classification of Fiber Laser Cutters: Types and Features
Choosing the right fiber laser cutting machine can be daunting given the wide range of models and features available. This article will guide you through the selection process by categorizing machines based on power, format size, and cutting capabilities. We will also examine the pros and cons of each model to help you make an informed decision and find the perfect machine to meet your cutting needs.
1 Classification by Power
When we talk about the power of a laser cutter, we are referring to the power of the laser source. To accommodate various materials and thicknesses, cutters with different power levels have been developed over time.
1.1 Low-Power Laser Cutter (1500W – 3000W)
Low-power fiber laser machines are suitable for cutting thin materials like stainless steel, carbon steel and aluminum. These machines are cost-effective and provide high precision but are limited to cutting thinner materials, typically up to 12mm.
Advantages:
Lower initial investment
Suitable for small businesses and hobbyists
Ideal for thin metal sheets and detailed designs
Disadvantages:
Limited cutting thickness (up to 12mm)
Slower cutting speeds for thicker materials
1.2 Mid-Power Laser Cutter (6000W – 8000W)
Mid-power machines are versatile, offering the ability to cut both thin and medium-thickness materials. They are often used in industries like automotive manufacturing and metal fabrication, handling materials up to 20mm thick.
Advantages:
Versatility for various materials and thicknesses
Faster cutting speeds compared to low-power machines
Suitable for medium-sized production runs
Disadvantages:
Limited cutting thickness (up to 20mm)
Increased energy consumption
1.3 High-Power Laser Cutter (12000W – 80000W)
High-power laser cutters are designed for cutting thick and dense materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel, with thicknesses over 200mm. These machines are commonly used in heavy-duty industries like aerospace and shipbuilding.
Advantages:
Can cut very thick materials with high precision
Fast cutting speeds even for dense metals
Ideal for large-scale industrial applications
Disadvantages:
Extremely high initial investment
Higher energy consumption
Maintenance costs may be significant due to high-power components
2 Classification by Format Size
The format size of CNC fiber laser cutters refers to the size of the cutting bed or working area, which dictates the maximum material dimensions the machine can handle.
2.1 Standard–Format Laser Cutter
These machines typically have cutting bed sizes ranging from 1300mm x 1300mm to 6000mm x 2500mm. Standard format cutting machines can meet most sheet metal processing needs, such as those required for electrical control cabinets, kitchenware, and the sheet metal fabrication industry.
Advantages:
Compact size, ideal for small workshops
Lower energy consumption
Suitable for precision work
Short production period
Easy maintenance
Disadvantages:
Limited cutting area, not suitable for all industries
Lower efficiency for specific tasks
2.2 Large–Format Laser Cutter
Large format machines have large bed sizes up to 26000mm*4000mm. These machines feature lower base for easy loading and unloading, suitable for large-scale industrial operations, such as shipbuilding or heavy equipment manufacturing.
Advantages:
Can handle oversized materials
Suitable for large-scale production
High productivity for mass manufacturing
Lower base for easy loading and unloading
Detachable for easy transportation
Disadvantages:
Requires significant floor space
High energy consumption
Expensive to purchase and maintain
2.3 Customized-Format Cutter
If standard format cutting machines do not meet your specific cutting requirements, manufacturers offer customized cutting formats tailored to your needs. By opting for a bespoke cutting solution, you can ensure that the machine accommodates unique material sizes and thicknesses, enhancing efficiency and precision in your operations.
Advantages:
Tailored to specific needs
Reduce the need for additional processing or secondary operations
Disadvantages:
Higher initial cost
Longer lead time
3 Classification by Structure
To meet diverse processing requirements and varying levels of automation, there are numerous models of laser cutting machines available. These models are designed to accommodate different material types, thicknesses, and production volumes, offering a range of features from basic manual controls to advanced automated systems.
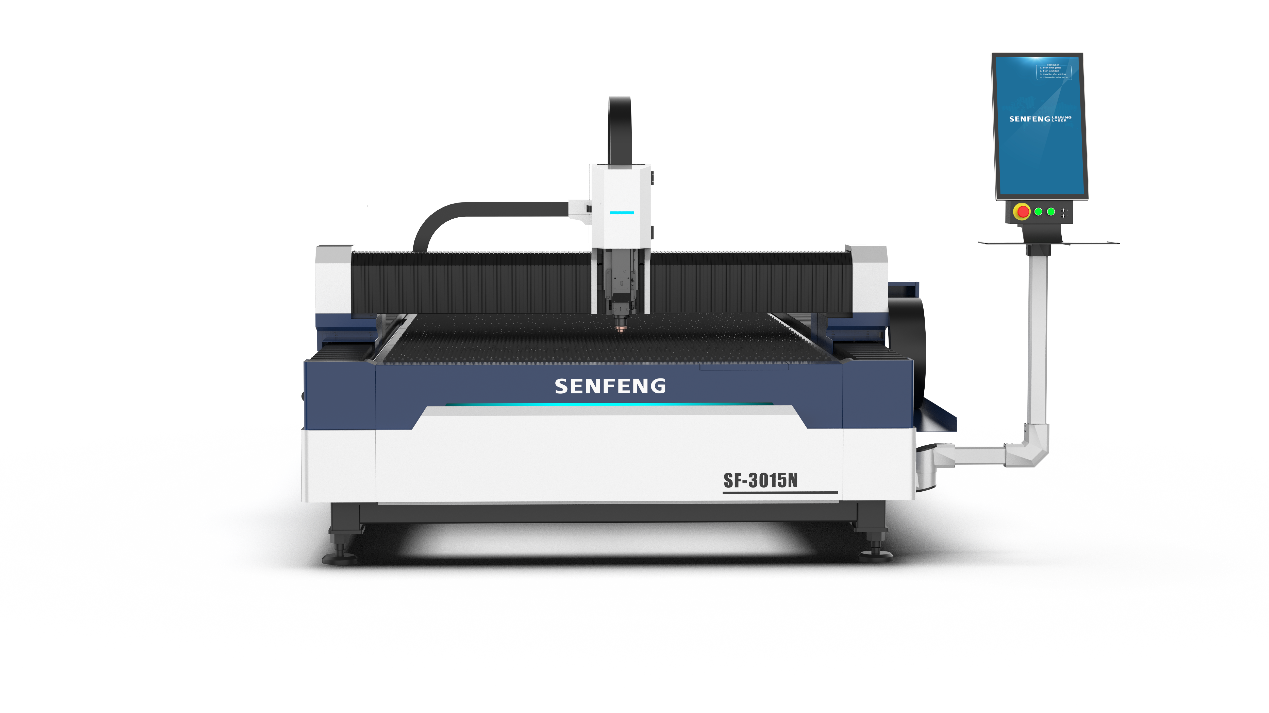
3.1 Open-Type Laser Cutter
Open machines are designed without a full enclosure, allowing operators easy access to the cutting area. These machines are typically less expensive and offer a good solution for cutting various materials.
See the picture below for the appearance of the equipment

Advantages:
Lower cost due to simpler design
Easier access for loading and unloading materials
Suitable for cutting larger materials that exceed the machine’s dimensions
Disadvantages:
Reduced safety, as the operator is exposed to laser radiation
More susceptible to environmental factors like dust and debris
Not suitable for industries with strict safety regulations
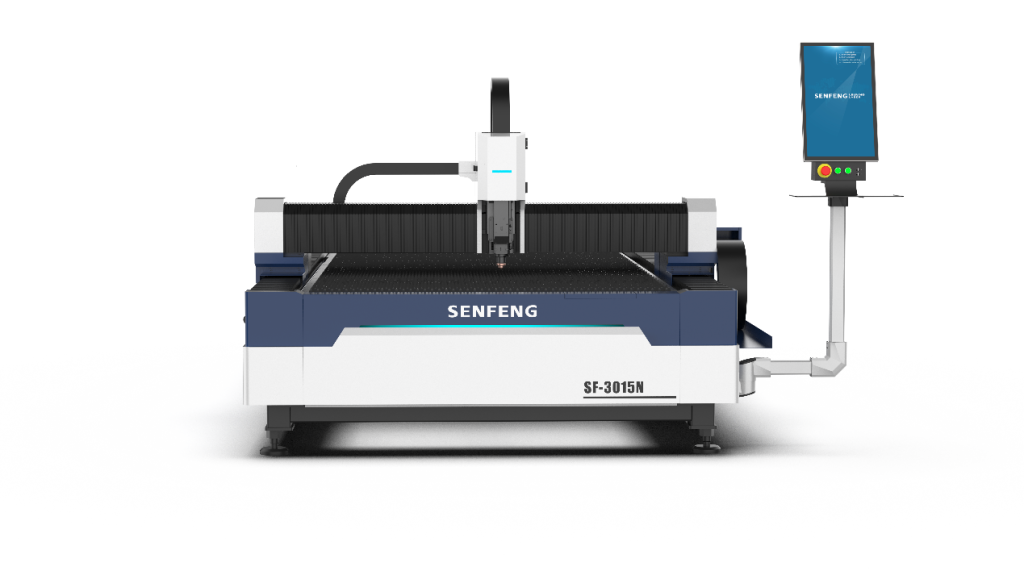
3.2 Enclosed Laser Cutter with Exchangeable Platform
Enclosed machines are fully covered, providing enhanced safety by containing the laser beam within a protective case. They also feature exchangeable platform for quick unloading and efficient cutting.
The appearance of the equipment is shown in the image below.

Advantages:
High level of safety, protecting the operator from laser radiation
Better control of environmental factors (e.g., dust, noise)
Often includes advanced ventilation and filtration systems
Exchangeable platform for quick unloading and efficient cutting
Disadvantages:
More expensive due to additional safety features
Less accessible for material handling
Limited ability to handle oversized materials
4 Classification by Cutting Functions
Different fiber laser cutting machines offer various cutting capabilities, such as metal sheet cutting, tube cutting, or both.
4.1 Metal Sheet Laser Cutter
Metal sheet laser cutters are among the most widely used machines, specifically designed for flat sheet cutting. They are capable of meeting the production needs of most clients by providing high precision and efficiency in cutting various metal sheets.
Advantages:
Excellent for cutting flat metal sheets
Fast and precise for 2D cutting
Widely available in different power (1.5-80 kW) and format sizes
Disadvantages:
Can only cut flat sheet material
Can only perform 90° vertical cuts on sheet material
4.2 Tube Laser Cutter
These machines are designed specifically for cutting round, square, and rectangular tubes and pipes. They are essential in industries like automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing.
Advantages:
Ideal for cutting tubes and pipes with high precision
Can handle complex geometric shapes
Specialized for industries needing tubular materials
Disadvantages:
More expensive than sheet metal laser cutting machines due to specialized design
4.3 Tube and Metal Sheet Laser Cutter
These versatile machines can cut both metal sheets and pipes, offering dual functionality in a single unit. This high cost-performance ratio makes them ideal for customers who primarily need to cut metal sheets but occasionally require pipe cutting.
Advantages:
Versatile for both sheet and tube cutting
Reduces the need for multiple machines
Saves space and cost for businesses with diverse cutting needs
Disadvantages:
More expensive than single-function machines
The pipe cutting capabilities are limited to standard sizes
The pipe cutting capability is not as advanced as that of specialized laser pipe cutting machines.
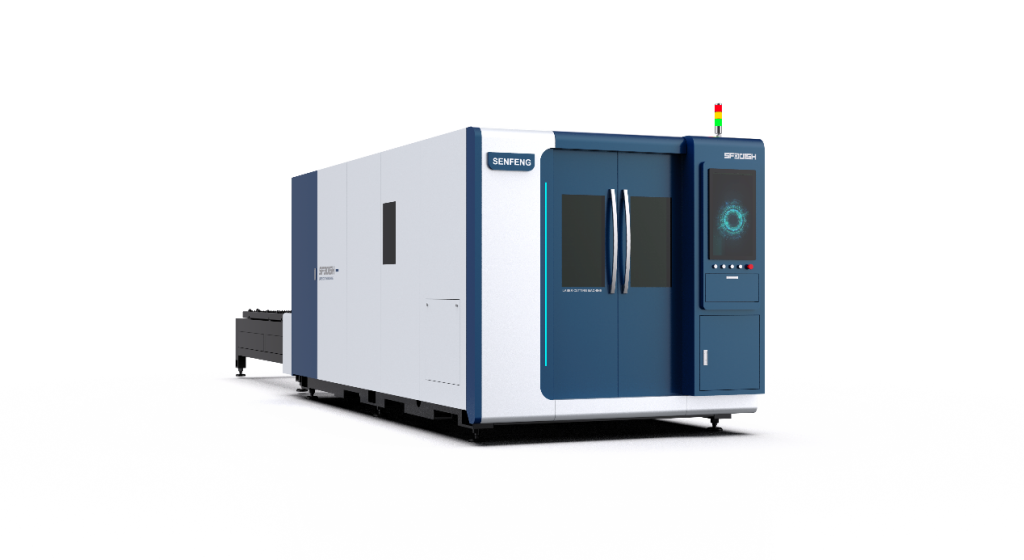
4.4 3D Laser Cutter
These machines can cut three-dimensional workpieces and are frequently used in industries such as automotive, construction, oil and gas, and coal mining.
The appearance of the 3D laser cutting machine is shown below

The 3D cutting samples are shown below




Advantages:
Can handle complex three-dimensional geometries
High precision and accuracy
Reduce the subsequent bending, welding and other processes
Disadvantages:
Higher initial cost
Complex operation and maintenance
4.5 Bevel Laser Cutter
These machines are used for cutting flat sheet metal at ±40° angles, facilitating seamless welding and other post-processing tasks for users.
The cutting samples are shown below
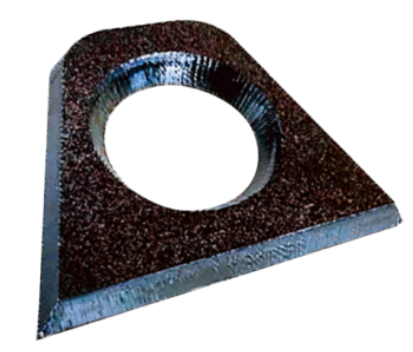
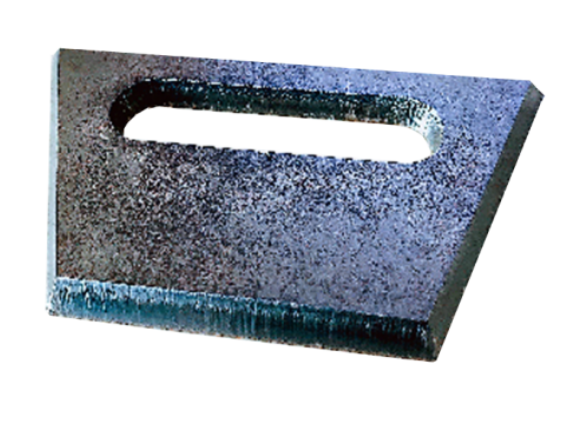
Advantages
Versatile angle cutting (±45°)
Reduced need for post-processing
High Precision when creating angled edges. Essential for applications like seamless welding and complex assembly.
Disadvantages
High initial cost
Limitations on thickness
Conclusion
Fiber laser cutting machines come in various types, classified by power, format size, enclosure type, and cutting function. Low-power machines are cost-effective and suitable for thin materials, while high-power machines are ideal for cutting thick metals in heavy industries. Small format machines are compact and precise, while large format machines handle oversized materials. Open machines offer easy access but lower safety, whereas enclosed machines provide enhanced protection at a higher cost. Finally, flatbed machines excel in 2D cutting, while tube cutting machines are specialized for pipes and tubes.
By understanding these classifications and their advantages and disadvantages, you can select the right fiber laser cutting machine that fits your business needs and budget.

